Why early detection matters ?
HCC is the most common primary liver cancer and one of the deadliest: in 2020, an estimated 905,700 people were diagnosed and 830,200 died worldwide.¹ Survival changes dramatically with stage, detecting HCC early can more than triple 5-year survival compared with late discovery.²
The current standard and its blind spots
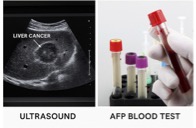
Ultrasound (US) ± AFP blood tests remains the backbone of surveillance every 6 months for at-risk patients in major guidelines.³ But both tools struggle with early tumors, obesity/MASLD, and coarse echotexture:
| ~45% US detects 45-52% of early HCC | ~63% US+AFP 63-74% improved Sensitivity | ~41-65% AFP by itself misses many cancers | <40% AFP underperforms in early stages |
US±AFP saves lives but still misses a clinically meaningful fraction of early cancers, exactly where detection helps most. Current US/EASL/AASLD guidance continues to recommend US ± AFP while acknowledging these limits.⁴
Advanced imaging like CT and MRI play an important role in confirming liver cancer, but they are costly, impractical for routine 6-month screening, and often miss smaller tumors under 2cm.5
OUR NEW BIOMARKER
LC-SPIK: Pioneering the Next Generation of Liver Cancer Diagnostics
At ImCare Biotech, we developed liver cancer-specific Serine Protease Inhibitor Kazal (LC-SPIK), a new blood biomarker designed to catch liver cancer (HCC) at its earliest stages when treatment works best. Unlike the regular form of SPIK (a common protein that rises during inflammation or in the pancreas), LC-SPIK is uniquely released by liver cancer cells making it far more specific to HCC.
What’s more, the predicted role of LC-SPIK is to help cancer cells evade from the body’s natural immune defenses, linking it directly to how liver cancer develops and ultimately helping in early diagnosis. By creating the Seravue® ELISA test, which only detects this cancer-specific version of SPIK, ImCare ensures that high LC-SPIK levels point to liver cancer. In multi-site and independent cohorts, LC-SPIK has consistently outperformed AFP especially in early HCC and AFP-negative disease.6,7
Key Highlights
Prospective, multi-center study (n=488; 164 HCC; 324 controls spanning cirrhosis and chronic HBV/HCV):
- All HCC vs liver disease controls:
- LC-SPIK AUC 0.87; 80% sensitivity / 90% specificity
- AFP AUC 0.70; 52% sensitivity / 86% specificity
- Early-stage (BCLC 0–A): LC-SPIK AUC 0.85; 72%/90% vs AFP AUC 0.61; 42%/86%.
- AFP-negative HCC: LC-SPIK correctly detected ~71% of cases missed by AFP.
NAFLD cirrhosis cohort (n=120):
- All HCC: LC-SPIK AUC 0.841; performance holds in early HCC (AUC 0.832).
- AFP-negative subgroup: LC-SPIK AUC 0.908.
- Combinations: LC-SPIK + PIVKA-II (DCP) AUC 0.926; LC-SPIK + AFP + PIVKA-II AUC 0.932 (highest), underscoring complementary biology.8
Our New Research Use Only* LC-SPIK kits are now commercially available.

*For Research Use Only. Not for Use in Diagnostic Procedures.
WHAT THIS MEANS FOR LIVER CANCER DIAGNOSTICS
Early Studies Show LC-SPIK is Different:
- Cancer-Specific Biology – Detects an HCC-unique SPIK form improving the diagnostic accuracy
- Early-stage performance – Maintains high accuracy where US/AFP historically underperform.
- Works when AFP is Negative – Strong detection in AFP-negative patients an area of persistent unmet need.
- Plays well with other biomarker – Synergizes with DCP (PIVKA-II) and AFP to push overall sensitivity into the 0.90+ range.7
 For Surveillance Programs | LC-SPIK can augment US±AFP, especially in hard-to-image patients (obesity/MASLD) and those with normal AFP. This could translate to more early finds, more curative options, and better outcomes. |
 Diagnostic Pathways | Panels that include LC-SPIK with AFP and DCP (PIVKA-II) provide strong, complementary signals that improve overall accuracy and robustness. |
Improved Health | Earlier, more accurate diagnosis reduces downstream cost and complexity (late-stage therapies, complications), a shift that benefits both patients treatment anxiety and economic burden. |

LC-SPIK is an investigational biomarker and is not approved yet by the FDA for clinical diagnostic use. Unlike AFP, LC-SPIK biomarker analysis is presently available for research use only. The information shared here is intended for educational purposes and not as medical advice.
LEARN MORE
Connect with Us Today
| Our Website | www.imcarebiotech.com |
| Our e-mail | info@imcarebiotech.com |
| Telephone | 215-489-4906 |
| HQ Address | 3805 Old Easton Road, Doylestown, PA 18902, USA |
| Social Media Handle | linkedin.com/company/imcare-biotech/ |
References
- Sung, H., Ferlay, J., Siegel, R. L., Laversanne, M., Soerjomataram, I., Jemal, A., & Bray, F. (2021). Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians, 71(3), 209-249.
- Yang, J. D. (2019). Detect or not to detect very early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma? The western perspective. Clinical and molecular hepatology, 25(4), 335.
- Tzartzeva, K., Obi, J., Rich, N. E., Parikh, N. D., Marrero, J. A., Yopp, A., … & Singal, A. G. (2018). Surveillance imaging and alpha fetoprotein for early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis: a meta-analysis. Gastroenterology, 154(6), 1706-1718.
- Wang, T., & Zhang, K. H. (2020). New blood biomarkers for the diagnosis of AFP-negative hepatocellular carcinoma. Frontiers in Oncology, 10, 1316.Lu, F., Shah, P. A., Rao, A., Gifford-Hollingsworth, C., Chen, A., Trey, G., … & Lu, X. (2020). Liver Cancer-Specific Serine Protease Inhibitor Kazal Is a Potentially Novel Biomarker for the Early Detection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clinical and translational gastroenterology, 11(12), e00271.
- Singal, A. G., Llovet, J. M., Yarchoan, M., Mehta, N., Heimbach, J. K., Dawson, L. A., … & Taddei, T. H. (2023). AASLD Practice Guidance on prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology, 78(6), 1922-1965.
- Lu, F., Shah, P. A., Rao, A., Gifford-Hollingsworth, C., Chen, A., Trey, G., … & Lu, X. (2020). Liver Cancer-Specific Serine Protease Inhibitor Kazal Is a Potentially Novel Biomarker for the Early Detection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clinical and translational gastroenterology, 11(12), e00271.
- Lu, F., Ott, C., Bista, P., & Lu, X. (2024). Three-Dimensional Structure of Novel Liver Cancer Biomarker Liver Cancer-Specific Serine Protease Inhibitor Kazal (LC-SPIK) and Its Performance in Clinical Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC). Diagnostics, 14(7), 725.
- Caviglia, G. P., Nicolosi, A., Abate, M. L., Carucci, P., Rosso, C., Rolle, E., … & Bugianesi, E. (2022). Liver cancer-specific isoform of serine protease inhibitor kazal for the detection of hepatocellular carcinoma: results from a pilot study in patients with dysmetabolic liver disease. Current Oncology, 29(8), 5457-5465.